Các nhà khoa học nghiên cứu các lõi ngô cổ được tìm thấy tại một địa điểm khảo cổ người Mỹ bản địa đã tìm thấy một loại virus 1.000 năm tuổi, loại virus thực vật cổ nhất từng được báo cáo.

Các cư dân cổ ở Antelope House, thuộc đài tượng niệm quốc gia Arizona's Canyon de Chelly đã trồng các loại cây như ngô, đậu và bí.
Ảnh được chụp bởi National Parks Service
Chỉ có một vài virus ARN đã được phát hiện trước đây từ các mẫu khảo cổ học, loại có niên đại lâu đời nhất từ khoảng 750 năm trước. Phát hiện mới được đưa ra khi nhóm các nhà khoa học nghiên cứu các tàn tích thực vật cổ từ Antelope House, một tàn tích của tổ tiên người da đỏ (Ancestral Puebloan) nằm ở Di tích Quốc gia Canyon de Chelly, Arizona.
Tổ tiên người da đỏ sống ở hẻm núi trồng các loại cây trồng như ngô, đậu và bí. Trong cuộc khai quật Nhà Antelope của Dịch vụ Công viên Quốc gia (National Park Service ) vào những năm 1970, hơn hai tấn tàn tích thực vật, ở dạng rất dễ nhận biết, đã được phục dựng.
Người đứng đầu nghiên cứu này, Marilyn Roossinck, giáo sư nghiên cứu bệnh học thực vật và vi sinh vật học môi trường, Đại học Khoa học Nông nghiệp, bang Penn cho biết: “rõ ràng từ những tàn tích thực vật này ngô là nguồn thức ăn chính của những cư dân nơi đây”.
Những tàn tích ngô được thu hồi tại Antelope House bao gồm lõi ngô, vỏ hạt ngô, lá, phần thân và râu ngô
Sử dụng phương pháp xác định niên đại C14, các nhà nghiên cứu đã xác nhận rằng tuổi của các mẫu cổ trên là khoảng 1.000 năm. Trong khi phân tích lõi ngô, các nhà khoa học đã phân tích 3 bộ gennome gần như toàn vẹn của loài virus chưa từng được biết trước đây, thuộc họ Chrysoviridae, nhóm virus lây nhiễm cho thực vật và nấm.


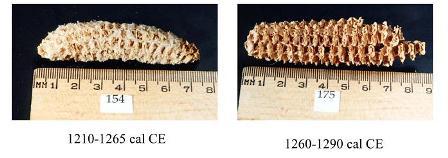
Niên C14 đã hiệu chỉnh của các mẫu lõi ngô (Mahtab Peyambari và cs, 2018)
Các nhà nghiên cứu đã đưa những phát hiện gần đây này của họ trên Tạp chí Virus học (Journal of Virology ) và lưu ý rằng chrysovirus là những virus thực vật tồn tại dai dẳng được truyền từ thế hệ này sang thế hệ khác thông qua hạt giống và có thể tồn tại trong vật chủ trong thời gian rất dài. Các virus tồn tại dai dẳng thường không gây bệnh và hiếm khi được phát hiện. Đây là loại chrysovirus đầu tiên được mô tả từ ngô, Roossinck lưu ý.
"Khi chúng tôi phân tích các mẫu ngô hiện đại, chúng tôi đã tìm thấy chrysovirus tương tự chỉ với khoảng 3 phần trăm biến dị so với các mẫu cổ xưa", cô nói. "Hầu hết các virus ARN, với thời gian thế hệ ngắn và sao chép dễ bị lỗi, phát triển nhanh chóng. Tuy nhiên, các virus dai dẳng có bộ gen rất ổn định."
Roossinck cho biết khía cạnh thú vị nhất từ những phát hiện này của nhóm nghiên cứu đó là virus đã tồn tại trong ngô từ rất lâu.
Cô cho biết thêm "Điều đó ngụ ý rằng virus có thể mang lại một số lợi ích tiềm ẩn cho thực vật, nhưng chúng tôi chưa chỉ ra được điều đó".
Nguồn:
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2018/12/181213112111.htm
Người dịch: Minh Trần

Các cư dân cổ ở Antelope House, thuộc đài tượng niệm quốc gia Arizona's Canyon de Chelly đã trồng các loại cây như ngô, đậu và bí.
Ảnh được chụp bởi National Parks Service
Chỉ có một vài virus ARN đã được phát hiện trước đây từ các mẫu khảo cổ học, loại có niên đại lâu đời nhất từ khoảng 750 năm trước. Phát hiện mới được đưa ra khi nhóm các nhà khoa học nghiên cứu các tàn tích thực vật cổ từ Antelope House, một tàn tích của tổ tiên người da đỏ (Ancestral Puebloan) nằm ở Di tích Quốc gia Canyon de Chelly, Arizona.
Tổ tiên người da đỏ sống ở hẻm núi trồng các loại cây trồng như ngô, đậu và bí. Trong cuộc khai quật Nhà Antelope của Dịch vụ Công viên Quốc gia (National Park Service ) vào những năm 1970, hơn hai tấn tàn tích thực vật, ở dạng rất dễ nhận biết, đã được phục dựng.
Người đứng đầu nghiên cứu này, Marilyn Roossinck, giáo sư nghiên cứu bệnh học thực vật và vi sinh vật học môi trường, Đại học Khoa học Nông nghiệp, bang Penn cho biết: “rõ ràng từ những tàn tích thực vật này ngô là nguồn thức ăn chính của những cư dân nơi đây”.
Những tàn tích ngô được thu hồi tại Antelope House bao gồm lõi ngô, vỏ hạt ngô, lá, phần thân và râu ngô
Sử dụng phương pháp xác định niên đại C14, các nhà nghiên cứu đã xác nhận rằng tuổi của các mẫu cổ trên là khoảng 1.000 năm. Trong khi phân tích lõi ngô, các nhà khoa học đã phân tích 3 bộ gennome gần như toàn vẹn của loài virus chưa từng được biết trước đây, thuộc họ Chrysoviridae, nhóm virus lây nhiễm cho thực vật và nấm.



Niên C14 đã hiệu chỉnh của các mẫu lõi ngô (Mahtab Peyambari và cs, 2018)
Các nhà nghiên cứu đã đưa những phát hiện gần đây này của họ trên Tạp chí Virus học (Journal of Virology ) và lưu ý rằng chrysovirus là những virus thực vật tồn tại dai dẳng được truyền từ thế hệ này sang thế hệ khác thông qua hạt giống và có thể tồn tại trong vật chủ trong thời gian rất dài. Các virus tồn tại dai dẳng thường không gây bệnh và hiếm khi được phát hiện. Đây là loại chrysovirus đầu tiên được mô tả từ ngô, Roossinck lưu ý.
"Khi chúng tôi phân tích các mẫu ngô hiện đại, chúng tôi đã tìm thấy chrysovirus tương tự chỉ với khoảng 3 phần trăm biến dị so với các mẫu cổ xưa", cô nói. "Hầu hết các virus ARN, với thời gian thế hệ ngắn và sao chép dễ bị lỗi, phát triển nhanh chóng. Tuy nhiên, các virus dai dẳng có bộ gen rất ổn định."
Roossinck cho biết khía cạnh thú vị nhất từ những phát hiện này của nhóm nghiên cứu đó là virus đã tồn tại trong ngô từ rất lâu.
Cô cho biết thêm "Điều đó ngụ ý rằng virus có thể mang lại một số lợi ích tiềm ẩn cho thực vật, nhưng chúng tôi chưa chỉ ra được điều đó".
Nguồn:
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2018/12/181213112111.htm
Người dịch: Minh Trần
Bằng chứng sớm nhất về một bức họa tạo bởi người Homo sapiens được tìm thấy trong hang Blombos phía nam Cape, Nam Phi.

Đây là cảnh bên ngoài hang Blombos ở phía nam Cape, Nam Phi. Ảnh được chụp bởi Magnus Haaland
Bức họa bao gồm ba vạch đỏ khắc chéo song song với sáu vạch riêng biệt, được vẽ một cách có chủ ý trên một mảnh tước silcrete nhẵn khoảng 73 000 năm trước. Nó có trước bức họa trước đó từ Châu Phi, Châu Âu và Đông Nam Á ít nhất 30 000 năm.
Bức họa trên mảnh tước silcrete là một phát hiện đáng ngạc nhiên của nhà khảo cổ học Ts. Luca Pollarolo, Đại học Witwatersrand (Wits), trong khi ông nghiên cứu tỉ mỉ hàng ngàn mảnh tương tự được khai quật từ Hang Blombos tại phòng thí nghiệm vệ tinh Wits, thị trấn Cape.

Bức họa hang Blombos bằng chì thổ hoàng trên đá silcrete. Ảnh được chụp bởi Craig Foster
Hang Blombos đã được khai quật bởi Giáo sư Christopher Henshilwood và Tiến sĩ Karen van Niekerk từ năm 1991. Địa điểm này có các hiện vật có niên đại từ 100 000 - 70 000 năm cách đây (thời kỳ đá giữa), cũng như hiện vật có niên đại từ 2000 - 300 năm cách đây.
Henshilwood người đứng đầu nghiên cứu tại Đại học Witwatersrand ở Nam Phi, và là Giám đốc của một Trung tâm Xuất sắc mới được tài trợ tại Đại học Bergen - Trung tâm Hành vi Sapiens sớm (SapienCE). Van Niekerk là điều tra viên chính tại SapienCE. Phát hiện của nhóm nghiên cứu về bức họa 73 000 năm tuổi đã được công bố trên tạp chí có sức ảnh hưởng lớn- tạp chí Nature, vào ngày 12 tháng 9.
Nhận ra rằng các đường kẻ trên mảnh tước không giống như bất cứ thứ khác mà nhóm đã nghiên cứu từ hang động trước đó, họ đã vạch ra câu trả lời cho các câu hỏi đặt ra. Những đường kẻ này là tự nhiên, hay là một phần các đường cấu tạo của đá? Có phải chúng được tạo ra bởi những người sống trong Hang Blombos 73 000 năm trước? Nếu con người tạo ra các đường kẻ này, thì làm thế nào họ tạo ra chúng, và tại sao?
Dưới sự hướng dẫn của Giáo sư Francesco d'Errico tại phòng thí nghiệm PACEA , Đại học Bordeaux, Pháp (tác giả thứ hai của bài báo), nhóm nghiên cứu đã kiểm tra và chụp ảnh mẫu đó dưới kính hiển vi để xác định xem liệu các đường đó có phải là một phần của đá hay chúng đã được vẽ trên đó. Để đảm bảo kết quả , họ cũng kiểm tra mẫu này bằng cách sử dụng phổ RAMAN và kính hiển vi điện tử. Sau khi xác nhận các đường được vẽ lên đá, nhóm nghiên cứu đã thử nghiệm nhiều kỹ thuật vẽ và sơn khác nhau và phát hiện ra rằng các nét vẽ đó được tạo ra bằng bút chì màu thổ hoàng, với đầu dày từ 1 đến 3 mm. Hơn nữa, việc kết thúc đột ngột các đường kẻ ở rìa của mảnh tước cũng gợi ý rằng mẫu vẽ ban đầu được mở rộng trên một bề mặt lớn hơn và có thể phức tạp hơn trong toàn bộ hình vẽ của nó.
ông Henshilwood cho biết: “Trước khi phát hiện ra, các nhà khảo cổ học nghiên cứu về thời đại Đá trong một thời gian dài đã bị thuyết phục rằng các biểu tượng không rõ ràng xuất hiện đầu tiên khi Homo sapiens vào châu Âu, khoảng 40 000 năm trước, và sau đó thay thế người Neanderthal bản địa. Những khám phá khảo cổ gần đây ở Châu Phi, Châu Âu và Châu Á, trong đó các thành viên trong nhóm của chúng tôi thường tham gia, hỗ trợ sự xuất hiện sớm hơn nhiều cho việc tạo ra và sử dụng các biểu tượng này.”
Khắc có lịch sử sớm hơn nhiều so với vẽ. Bức khắc sớm nhất được biết đến, một hình zig-zag, được khắc trên vỏ sò nước ngọt từ Trinil, Java, đã được tìm thấy trong các lớp có niên đại cách đây 54 0000 năm, trước khi người hiện đại biết đến, và được cho rằng được tạo bởi Homo erectus, một bài báo gần đây đã đề xuất rằng các hình vẽ trong ba hang động của Bán đảo Iberia là 64.000 tuổi và do đó được tạo ra bởi người Neanderthal. Điều này làm cho bản vẽ trên mảnh tước silcret ở Blombos trở thành bản vẽ cổ nhất của Homo sapiens từng được tìm thấy.
Mặc dù các biểu diễn trừu tượng và tượng hình thường được coi là các chỉ tiêu xác định việc sử dụng các biểu tượng, sự đánh giá kích thước biểu tượng của các hình vẽ này có thể là sớm nhất này thật sự khó khăn.
Các biểu tượng là một phần vốn có của nhân loại. Chúng có thể được khắc trên cơ thể chúng ta dưới dạng hình xăm và vết sẹo hoặc che chúng thông qua việc mặc quần áo, đồ trang sức và cách chúng ta để tóc.
Ngôn ngữ, chữ viết, toán học, tôn giáo, luật pháp không thể tồn tại nếu thiếu khả năng đặc biệt của con người để làm chủ việc tạo, truyền tải các biểu tượng và khả năng của chúng ta thể hiện chúng trong văn hóa vật chất. Sự tiến bộ đáng kể đã được thực hiện để hiểu cách não bộ của chúng ta nhận thức và xử lý các loại biểu tượng khác nhau, nhưng kiến thức về cách thức và thời điểm các biểu tượng chứa đậm văn hóa của tổ tiên chúng ta vẫn còn thiếu chính xác và chỉ là phỏng đoán.
Lớp khảo cổ học trong đó bức họa Blombos được tìm thấy cũng mang lại những biểu trưng khác về tư duy biểu tượng, chẳng hạn như các hạt chuỗi vỏ sò được phủ bằng thổ hoàng, và quan trọng hơn là các mảnh thổ hoàng được khắc hoa văn trừu tượng. Một số trong những bản khắc này gần giống với những nét vẽ trên mảnh tước silcret.
Henshilwood cho biết: “Điều này chứng tỏ rằng Homo sapiens sớm ở phía nam Cape đã sử dụng các kỹ thuật khác nhau để tạo ra các dấu hiệu tương tự trên các phương tiện truyền thông khác nhau. Quan sát trên ủng hộ giả thuyết rằng những dấu hiệu này có tính chất tượng trưng và thể hiện một khía cạnh vốn có của thế giới hiện đại về hành vi của những người Homo sapiens châu Phi này, tổ tiên của tất cả chúng ta ngày nay.
Nguồn: https://www.heritagedaily.com/2018/12/top-10-archaeological-discoveries-of-2018/122316
https://www.heritagedaily.com/2018/09/multimedia-graphic-design-73000-years-ago/121644
https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/anthropology-in-practice/73-000-year-old-hashtag-is-oldest-example-of-abstract-art/
Người dịch: Minh Trần
Tại một địa điểm khảo cổ ở phía đông bắc Jordan, các nhà nghiên cứu đã phát hiện ra tàn tích tro than của bánh mì dẹt nướng bởi những người săn bắn hái lượm cách đây 14.400 năm.

Một trong những cấu trúc bằng đá của di chỉ Shubayqa 1. Lò nướng, nơi bánh mì được tìm thấy, ở giữa. Ảnh chụp bởi Alexis Pantos
Đây là bằng chứng trực tiếp lâu đời nhất về bánh mì được tìm thấy cho đến nay, trước sự ra đời của nông nghiệp ít nhất 4.000 năm. Các phát hiện cho thấy việc sản xuất bánh mì dựa trên ngũ cốc hoang dại có thể đã khuyến khích những người săn bắt hái lượm trồng ngũ cốc, và do đó đã đóng góp cho cuộc cách mạng nông nghiệp trong thời kỳ Đá mới.
Một nhóm các nhà nghiên cứu từ Đại học Copenhagen, Đại học College London và Đại học Cambridge đã phân tích phần còn lại thức ăn bị cháy thành than từ một địa điểm săn bắn hái lượm Natufian 14.400 tuổi – di chỉ Shubayqa 1 thuộc sa mạc Đen ở đông bắc Jordan. Các kết quả, được công bố trên tạp chí Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, cung cấp bằng chứng thực nghiệm sớm nhất cho việc sản xuất bánh mì.
Amaia Arranz Otaegui, chuyên gia cổ thực vật của Đại học Copenhagen, tác giả đầu tiên của nghiên cứu cho biết:
“Sự có mặt của hàng trăm tàn tích tro than thức ăn trong các bếp lửa ở di chỉ Shubayqa 1 là một phát hiện đặc biệt, và nó đã cho chúng tôi cơ hội để mô tả các thực hành thực phẩm 14.000 năm tuổi. 24 tàn tích được phân tích trong nghiên cứu này cho thấy tổ tiên hoang dại của các loại ngũ cốc được thuần hóa như lúa mạch, bạch quả và yến mạch đã được nghiền, sàng và nhào trước khi nấu. Phần còn lại rất giống với bánh mì dẹt không có men được xác định tại một số địa điểm thời kì Đá mới và La Mã ở châu Âu và Thổ Nhĩ Kỳ. Vì vậy, bây giờ chúng ta biết rằng các sản phẩm giống như bánh mì đã được sản xuất từ lâu trước khi phát triển nông nghiệp. Bước tiếp theo là đánh giá xem việc sản xuất và tiêu thụ bánh mì có ảnh hưởng đến sự xuất hiện của trồng trọt và thuần hóa cây trồng hay không?"
Nhà khảo cổ học Tobias Richter , Đại học Copenhagen, người đứng đầu cuộc khai quật Shubayqa 1 ở Jordan, đã giải thích:
Những người săn bắn hái lượm Natufian là mối quan tâm đặc biệt đối với chúng tôi vì họ đã sống qua một thời kỳ chuyển tiếp khi con người trở nên ít di chuyển hơn và chế độ ăn uống của họ bắt đầu thay đổi. Các phiến tước đá lửa hình liềm cũng như các công cụ đá mài được tìm thấy tại các địa điểm Natufian ở Levant từ lâu đã khiến các nhà khảo cổ nghi ngờ rằng con người đã bắt đầu khai thác thực vật theo một cách khác và có lẽ hiệu quả hơn. Nhưng bánh mì dẹt được tìm thấy tại Shubayqa 1 là bằng chứng sớm nhất về việc làm bánh mì được phục dựng cho đến nay, và nó cho thấy nướng bánh đã được phát minh trước khi chúng ta trồng trọt. Vì vậy, bằng chứng này xác nhận một số ý tưởng của chúng tôi. Thật vậy, có thể việc sản xuất bánh mì sớm và cực kỳ tốn thời gian dựa trên ngũ cốc hoang dại có thể là một trong những động lực chính của cuộc cách mạng nông nghiệp sau này, ở đó ngũ cốc hoang dã được trồng để cung cấp nguồn thực phẩm thuận tiện hơn.
Các mẫu than dưới kính hiển vi
Các tàn tích tro thức ăn được phân tích bằng kính hiển vi điện tử tại phòng thí nghiệm của Đại học London bởi Nghiên cứu sinh Lara Gonzalez Carratero (Viện Khảo cổ Đại học Luân Đôn), một chuyên gia về bánh mì thời tiền sử: Ông cho biết:
“Việc xác định ‘bánh mì ’ hoặc các sản phẩm dựa trên ngũ cốc khác trong khảo cổ học không đơn giản. Đã có xu hướng đơn giản hóa việc phân loại mà không cần thực sự kiểm tra nó theo tiêu chí xác định. Chúng tôi đã thiết lập một bộ tiêu chí mới để xác định bánh mì dẹt, bột và cháo giống như các sản phẩm trong ghi nhận khảo cổ học. Sử dụng Kính hiển vi điện tử quét, chúng tôi đã xác định được các vi cấu trúc và các hạt của từng loại tro thực phẩm”
Theo Giáo sư Dorian Fuller (Viện Khảo cổ Đại học Luân Đôn):“Bánh mì liên quan quá trình lao động chế biến bao gồm xay ngũ cốc (tách bỏ vỏ), nghiền ngũ cốc và nhào và nướng. Rằng nó được sản xuất trước khi các phương pháp canh tác cho thấy nó được coi là đặc biệt, và mong muốn tạo ra nhiều thực phẩm đặc biệt này có lẽ đã góp phần vào quyết định bắt đầu trồng ngũ cốc. Tất cả những điều này phụ thuộc vào sự phát triển phương pháp mới cho phép chúng ta xác định phần còn lại của bánh mì từ những mảnh than cháy rất nhỏ bằng sự phóng đại cao”,
Nghiên cứu về thực hành thực phẩm thời tiền sử vẫn tiếp tục
Một quĩ tài trợ gần đây được trao cho nhóm Đại học Copenhagen sẽ đảm bảo rằng nghiên cứu về sản xuất thực phẩm trong giai đoạn chuyển sang thời kỳ Đá mới sẽ tiếp tục:
ông Tobias Richter cho hay:
“Hội đồng nghiên cứu độc lập của Đan Mạch gần đây đã phê duyệt tài trợ thêm cho công việc của chúng tôi, điều này sẽ cho phép chúng tôi điều tra chi tiết hơn cách mọi người tiêu thụ thực vật và động vật khác nhau. Dựa trên nghiên cứu của chúng tôi về bánh mì sớm, trong tương lai sẽ cho chúng ta biết rõ hơn lý do tại sao một số thành phần nhất định được ưa chuộng hơn những thành phần khác và cuối cùng được chọn để canh tác".
Nguồn: https://www.heritagedaily.com/2018/07/archaeologists-discover-bread-that-predates-agriculture-by-4000-years/120954
Người dịch: Minh Trần

Một trong những cấu trúc bằng đá của di chỉ Shubayqa 1. Lò nướng, nơi bánh mì được tìm thấy, ở giữa. Ảnh chụp bởi Alexis Pantos
Đây là bằng chứng trực tiếp lâu đời nhất về bánh mì được tìm thấy cho đến nay, trước sự ra đời của nông nghiệp ít nhất 4.000 năm. Các phát hiện cho thấy việc sản xuất bánh mì dựa trên ngũ cốc hoang dại có thể đã khuyến khích những người săn bắt hái lượm trồng ngũ cốc, và do đó đã đóng góp cho cuộc cách mạng nông nghiệp trong thời kỳ Đá mới.
Một nhóm các nhà nghiên cứu từ Đại học Copenhagen, Đại học College London và Đại học Cambridge đã phân tích phần còn lại thức ăn bị cháy thành than từ một địa điểm săn bắn hái lượm Natufian 14.400 tuổi – di chỉ Shubayqa 1 thuộc sa mạc Đen ở đông bắc Jordan. Các kết quả, được công bố trên tạp chí Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, cung cấp bằng chứng thực nghiệm sớm nhất cho việc sản xuất bánh mì.
Amaia Arranz Otaegui, chuyên gia cổ thực vật của Đại học Copenhagen, tác giả đầu tiên của nghiên cứu cho biết:
“Sự có mặt của hàng trăm tàn tích tro than thức ăn trong các bếp lửa ở di chỉ Shubayqa 1 là một phát hiện đặc biệt, và nó đã cho chúng tôi cơ hội để mô tả các thực hành thực phẩm 14.000 năm tuổi. 24 tàn tích được phân tích trong nghiên cứu này cho thấy tổ tiên hoang dại của các loại ngũ cốc được thuần hóa như lúa mạch, bạch quả và yến mạch đã được nghiền, sàng và nhào trước khi nấu. Phần còn lại rất giống với bánh mì dẹt không có men được xác định tại một số địa điểm thời kì Đá mới và La Mã ở châu Âu và Thổ Nhĩ Kỳ. Vì vậy, bây giờ chúng ta biết rằng các sản phẩm giống như bánh mì đã được sản xuất từ lâu trước khi phát triển nông nghiệp. Bước tiếp theo là đánh giá xem việc sản xuất và tiêu thụ bánh mì có ảnh hưởng đến sự xuất hiện của trồng trọt và thuần hóa cây trồng hay không?"
Nhà khảo cổ học Tobias Richter , Đại học Copenhagen, người đứng đầu cuộc khai quật Shubayqa 1 ở Jordan, đã giải thích:
Những người săn bắn hái lượm Natufian là mối quan tâm đặc biệt đối với chúng tôi vì họ đã sống qua một thời kỳ chuyển tiếp khi con người trở nên ít di chuyển hơn và chế độ ăn uống của họ bắt đầu thay đổi. Các phiến tước đá lửa hình liềm cũng như các công cụ đá mài được tìm thấy tại các địa điểm Natufian ở Levant từ lâu đã khiến các nhà khảo cổ nghi ngờ rằng con người đã bắt đầu khai thác thực vật theo một cách khác và có lẽ hiệu quả hơn. Nhưng bánh mì dẹt được tìm thấy tại Shubayqa 1 là bằng chứng sớm nhất về việc làm bánh mì được phục dựng cho đến nay, và nó cho thấy nướng bánh đã được phát minh trước khi chúng ta trồng trọt. Vì vậy, bằng chứng này xác nhận một số ý tưởng của chúng tôi. Thật vậy, có thể việc sản xuất bánh mì sớm và cực kỳ tốn thời gian dựa trên ngũ cốc hoang dại có thể là một trong những động lực chính của cuộc cách mạng nông nghiệp sau này, ở đó ngũ cốc hoang dã được trồng để cung cấp nguồn thực phẩm thuận tiện hơn.
Các mẫu than dưới kính hiển vi
Các tàn tích tro thức ăn được phân tích bằng kính hiển vi điện tử tại phòng thí nghiệm của Đại học London bởi Nghiên cứu sinh Lara Gonzalez Carratero (Viện Khảo cổ Đại học Luân Đôn), một chuyên gia về bánh mì thời tiền sử: Ông cho biết:
“Việc xác định ‘bánh mì ’ hoặc các sản phẩm dựa trên ngũ cốc khác trong khảo cổ học không đơn giản. Đã có xu hướng đơn giản hóa việc phân loại mà không cần thực sự kiểm tra nó theo tiêu chí xác định. Chúng tôi đã thiết lập một bộ tiêu chí mới để xác định bánh mì dẹt, bột và cháo giống như các sản phẩm trong ghi nhận khảo cổ học. Sử dụng Kính hiển vi điện tử quét, chúng tôi đã xác định được các vi cấu trúc và các hạt của từng loại tro thực phẩm”
Theo Giáo sư Dorian Fuller (Viện Khảo cổ Đại học Luân Đôn):“Bánh mì liên quan quá trình lao động chế biến bao gồm xay ngũ cốc (tách bỏ vỏ), nghiền ngũ cốc và nhào và nướng. Rằng nó được sản xuất trước khi các phương pháp canh tác cho thấy nó được coi là đặc biệt, và mong muốn tạo ra nhiều thực phẩm đặc biệt này có lẽ đã góp phần vào quyết định bắt đầu trồng ngũ cốc. Tất cả những điều này phụ thuộc vào sự phát triển phương pháp mới cho phép chúng ta xác định phần còn lại của bánh mì từ những mảnh than cháy rất nhỏ bằng sự phóng đại cao”,
Nghiên cứu về thực hành thực phẩm thời tiền sử vẫn tiếp tục
Một quĩ tài trợ gần đây được trao cho nhóm Đại học Copenhagen sẽ đảm bảo rằng nghiên cứu về sản xuất thực phẩm trong giai đoạn chuyển sang thời kỳ Đá mới sẽ tiếp tục:
ông Tobias Richter cho hay:
“Hội đồng nghiên cứu độc lập của Đan Mạch gần đây đã phê duyệt tài trợ thêm cho công việc của chúng tôi, điều này sẽ cho phép chúng tôi điều tra chi tiết hơn cách mọi người tiêu thụ thực vật và động vật khác nhau. Dựa trên nghiên cứu của chúng tôi về bánh mì sớm, trong tương lai sẽ cho chúng ta biết rõ hơn lý do tại sao một số thành phần nhất định được ưa chuộng hơn những thành phần khác và cuối cùng được chọn để canh tác".
Nguồn: https://www.heritagedaily.com/2018/07/archaeologists-discover-bread-that-predates-agriculture-by-4000-years/120954
Người dịch: Minh Trần
Chế độ dinh dưỡng của người Neandertal được tranh luận khá nhiều: theo truyền thống họ được coi là động vật ăn thịt và thợ săn các động vật có vú lớn, nhưng giả thuyết này gần đây đã bị thách thức bởi nhiều bằng chứng về sự tiêu thụ thực vật.

Răng của một cá thể Neandertal trưởng thành thuộc địa điểm Les Cottés, Pháp. Chế độ dinh dưỡng của cô chủ yêu là thịt các động vật ăn cỏ lớn. Ảnh chụp bởi A. Le Cabec.
Các chế độ dinh dưỡng cổ thường được phục dựng lại bằng cách sử dụng các tỷ lệ đồng vị nitơ, để xác định bậc dinh dưỡng, vị trí mà một sinh vật chiếm giữ trong chuỗi thức ăn. Người Neandertals dường như chiếm một vị trí cao trong chuỗi thức ăn trên cạn, thể hiện tỷ lệ cao hơn một chút so với động vật ăn thịt (như linh cẩu, chó sói hoặc cáo) được tìm thấy tại cùng địa điểm. Điều này gợi ý rằng những giá trị cao hơn một chút là do tiêu thụ voi ma mút hoặc thịt ôi. Và chúng tôi cũng biết một số ví dụ về ăn thịt đồng loại ở các địa điểm khác có người Neandertal.
Người hiện đại thời Đá cũ đã đến Pháp ngay sau khi người Neandertal biến mất, thể hiện tỷ lệ đồng vị nitơ cao hơn người Neandertal. Theo cách cổ điển, điều này chỉ thị cho sự tiêu thụ cá nước ngọt. Đánh bắt cá được cho là một hoạt động điển hình của người hiện đại, nhưng một lần nữa, một cuộc tranh luận đó là liệu người Neandertals có ăn các nguồn thủy sản hay không. Khi Klervia Jaouen, nhà nghiên cứu Nhân chủng học tiến hóa tại Viện Max Planck - tác giả đầu tiên của nghiên cứu, và các cộng tác viên đã phát hiện ra tỷ lệ đồng vị nitơ cao trong collagen của hai người Neandertal nằm trong giới hạn của người hiện đại, họ băn khoăn liệu đây có phải là sự xác nhận cho việc tiêu thụ cá thường xuyên?
Người Neandertals đến từ Les Cottés và Grotte du Renne, ở Pháp, hai địa điểm không tìm thấy di cốt cá. Tuy nhiên, các phép đo được thực hiện trên một phần chân răng để ghi lại chế độ dinh dưỡng từ 4 đến 8 năm của đời sống cá thể đó và trên một xương của một đứa trẻ 1 tuổi. Các tỷ lệ đồng vị nitơ cao này cũng có thể chỉ ra rằng người Neandertals không bị cai sữa ở độ tuổi trên, điều này trái ngược trong trường hợp Neandertal ở địa điểm Les Cottés (cá thể được phân tích chân răng) có những bằng chứng trước đây về việc cai sữa sớm khoảng một tuổi. Nói cách khác, nhiều sự giải thích (ví dụ như tiêu thụ cá nước ngọt, thịt ôi, cai sữa muộn hoặc thậm chí ăn thịt đồng loại) có thể giải thích cho các tỉ lệ đồng vị ni tơ cao như vậy và xác định yếu tố liên quan có thể thay đổi sự hiểu của chúng ta về phương thức sống của người Neandertal.
Phân tích axit amin
Để giải thích các tỷ lệ đồng vị nitơ đặc biệt cao này, Jaouen và các cộng tác viên đã quyết định sử dụng một kỹ thuật đồng vị mới độc đáo. Các phân tích đồng vị đặc trưng cho hợp chất (CSIA = Compound-specific isotope analyses) cho phép phân tích riêng các axit amin có trong collagen. Một số thành phần đồng vị axit amin bị ảnh hưởng bởi các yếu tố môi trường và các tỉ lệ đồng vị của thức ăn. Ngoài ra, các tỷ lệ đồng vị axit amin khác cũng bị ảnh hưởng bởi bậc dinh dưỡng. Sự kết hợp của các tỷ lệ đồng vị axit amin này cho phép giải mã sự đóng góp của môi trường và bậc dinh dưỡng đối với thành phần đồng vị cuối cùng của collagen.
Jaouen cho biết, “Sử dụng kỹ thuật này, chúng tôi phát hiện ra rằng người Neandertal của địa điểm Les Cottés có chế độ ăn thịt trên cạn hoàn toàn: cô không phải là một đứa trẻ cai sữa muộn hay là một người ăn cá thường xuyên, đồng loại của cô dường như chủ yếu săn bắt tuần lộc và ngựa. “Chúng tôi cũng xác nhận rằng Neandertal của địa điểm Grotte du Renne là một đứa trẻ bú sữa mẹ mà mẹ là một người ăn thịt. Thật thú vị, kết luận này phù hợp với các quan sát của các nhà khảo cổ.
Nghiên cứu trên cũng cho thấy tầm quan trọng của kỹ thuật đồng vị mới này đối với các nghiên cứu trong tương lai về chế độ dinh dưỡng của người Neandertal và người cổ. Sử dụng phân tích đồng vị đặc trưng cho hợp chất cho phép các nhà nghiên cứu không bị giải thích sai tỷ lệ đồng vị nitơ toàn cầu, đặc biệt cao. Michael P. Richards thuộc Đại học Simon Fraser ,Canada nhận xét: Những kết quả đồng vị trước đây cho thấy chế độ ăn thịt chủ yếu của người Neandertals, phù hợp với những ghi nhận khảo cổ rộng rãi về di cốt động vật được tìm thấy và được chôn bởi người Neandertals. Gần đây đã có một số giải thích thẳng thắn kì lạ về số lượng lớn dữ liệu đồng vị bao gồm cách giải thích người Neandertal chủ yếu sống dựa vào thực vật thủy sinh đến việc ăn thịt lẫn nhau, cả hai quan điểm này trái ngược với các bằng chứng khảo cổ học. Các phép đo đồng vị đặc trưng cho hợp chất mới này khẳng định lại các giải thích trước đây về chế độ ăn của người Neandertal bao gồm chủ yếu là động vật ăn cỏ lớn, mặc dù tất nhiên họ cũng tiêu thụ các loại thực phẩm khác như thực vật.
Chế độ dinh dưỡng đơn điệu
Ngoài việc xác nhận người Neandertal là động vật ăn thịt trên cạn, nghiên cứu này dường như chỉ ra rằng những Tông người này có chế độ ăn rất đơn điệu theo thời gian, ngay cả khi chúng đã bắt đầu thay đổi kĩ nghệ nguyên liệu, có thể dưới ảnh hưởng của người hiện đại. Em bé Neandertal của địa điểm Grotte du Renne được tìm thấy, thực sự có liên quan đến Châtelperronian, một kĩ nghệ đá tương tự như của người hiện đại. Do đó, người Neandertal muộn rất giống người hiện đại về các bức họa trong hang động và đeo vòng cổ, nhưng không giống như loài chị em của họ đó là dường như họ không thích đánh bắt cá.
Jean-Jacques Hublin, giám đốc Khoa Tiến hóa Người tại Viện Max Planck, nhận xét: “Nghiên cứu này xác nhận rằng khi người Homo sapiens đến châu Âu và gặp người Neandertal, họ đã cạnh tranh trực tiếp để khai thác các động vật có vú lớn “.Sahra Talamo- nhà nghiên cứu tại Viện Max Planck kết luận: “ Việc sử dụng hệ thống kết hợp các phân tích đồng vị đặc trưng cho hợp chất (CSIA) và định niên đại C sẽ giúp hiểu được liệu hai loài có thực sự có cùng một phương thức sinh kế trong những thời điểm quan trọng đó hay không.”
Nguồn: https://www.heritagedaily.com/2019/02/neandertals-main-food-source-was-definitely-meat/122703
Người dịch: Minh Trần

Răng của một cá thể Neandertal trưởng thành thuộc địa điểm Les Cottés, Pháp. Chế độ dinh dưỡng của cô chủ yêu là thịt các động vật ăn cỏ lớn. Ảnh chụp bởi A. Le Cabec.
Các chế độ dinh dưỡng cổ thường được phục dựng lại bằng cách sử dụng các tỷ lệ đồng vị nitơ, để xác định bậc dinh dưỡng, vị trí mà một sinh vật chiếm giữ trong chuỗi thức ăn. Người Neandertals dường như chiếm một vị trí cao trong chuỗi thức ăn trên cạn, thể hiện tỷ lệ cao hơn một chút so với động vật ăn thịt (như linh cẩu, chó sói hoặc cáo) được tìm thấy tại cùng địa điểm. Điều này gợi ý rằng những giá trị cao hơn một chút là do tiêu thụ voi ma mút hoặc thịt ôi. Và chúng tôi cũng biết một số ví dụ về ăn thịt đồng loại ở các địa điểm khác có người Neandertal.
Người hiện đại thời Đá cũ đã đến Pháp ngay sau khi người Neandertal biến mất, thể hiện tỷ lệ đồng vị nitơ cao hơn người Neandertal. Theo cách cổ điển, điều này chỉ thị cho sự tiêu thụ cá nước ngọt. Đánh bắt cá được cho là một hoạt động điển hình của người hiện đại, nhưng một lần nữa, một cuộc tranh luận đó là liệu người Neandertals có ăn các nguồn thủy sản hay không. Khi Klervia Jaouen, nhà nghiên cứu Nhân chủng học tiến hóa tại Viện Max Planck - tác giả đầu tiên của nghiên cứu, và các cộng tác viên đã phát hiện ra tỷ lệ đồng vị nitơ cao trong collagen của hai người Neandertal nằm trong giới hạn của người hiện đại, họ băn khoăn liệu đây có phải là sự xác nhận cho việc tiêu thụ cá thường xuyên?
Người Neandertals đến từ Les Cottés và Grotte du Renne, ở Pháp, hai địa điểm không tìm thấy di cốt cá. Tuy nhiên, các phép đo được thực hiện trên một phần chân răng để ghi lại chế độ dinh dưỡng từ 4 đến 8 năm của đời sống cá thể đó và trên một xương của một đứa trẻ 1 tuổi. Các tỷ lệ đồng vị nitơ cao này cũng có thể chỉ ra rằng người Neandertals không bị cai sữa ở độ tuổi trên, điều này trái ngược trong trường hợp Neandertal ở địa điểm Les Cottés (cá thể được phân tích chân răng) có những bằng chứng trước đây về việc cai sữa sớm khoảng một tuổi. Nói cách khác, nhiều sự giải thích (ví dụ như tiêu thụ cá nước ngọt, thịt ôi, cai sữa muộn hoặc thậm chí ăn thịt đồng loại) có thể giải thích cho các tỉ lệ đồng vị ni tơ cao như vậy và xác định yếu tố liên quan có thể thay đổi sự hiểu của chúng ta về phương thức sống của người Neandertal.
Phân tích axit amin
Để giải thích các tỷ lệ đồng vị nitơ đặc biệt cao này, Jaouen và các cộng tác viên đã quyết định sử dụng một kỹ thuật đồng vị mới độc đáo. Các phân tích đồng vị đặc trưng cho hợp chất (CSIA = Compound-specific isotope analyses) cho phép phân tích riêng các axit amin có trong collagen. Một số thành phần đồng vị axit amin bị ảnh hưởng bởi các yếu tố môi trường và các tỉ lệ đồng vị của thức ăn. Ngoài ra, các tỷ lệ đồng vị axit amin khác cũng bị ảnh hưởng bởi bậc dinh dưỡng. Sự kết hợp của các tỷ lệ đồng vị axit amin này cho phép giải mã sự đóng góp của môi trường và bậc dinh dưỡng đối với thành phần đồng vị cuối cùng của collagen.
Jaouen cho biết, “Sử dụng kỹ thuật này, chúng tôi phát hiện ra rằng người Neandertal của địa điểm Les Cottés có chế độ ăn thịt trên cạn hoàn toàn: cô không phải là một đứa trẻ cai sữa muộn hay là một người ăn cá thường xuyên, đồng loại của cô dường như chủ yếu săn bắt tuần lộc và ngựa. “Chúng tôi cũng xác nhận rằng Neandertal của địa điểm Grotte du Renne là một đứa trẻ bú sữa mẹ mà mẹ là một người ăn thịt. Thật thú vị, kết luận này phù hợp với các quan sát của các nhà khảo cổ.
Nghiên cứu trên cũng cho thấy tầm quan trọng của kỹ thuật đồng vị mới này đối với các nghiên cứu trong tương lai về chế độ dinh dưỡng của người Neandertal và người cổ. Sử dụng phân tích đồng vị đặc trưng cho hợp chất cho phép các nhà nghiên cứu không bị giải thích sai tỷ lệ đồng vị nitơ toàn cầu, đặc biệt cao. Michael P. Richards thuộc Đại học Simon Fraser ,Canada nhận xét: Những kết quả đồng vị trước đây cho thấy chế độ ăn thịt chủ yếu của người Neandertals, phù hợp với những ghi nhận khảo cổ rộng rãi về di cốt động vật được tìm thấy và được chôn bởi người Neandertals. Gần đây đã có một số giải thích thẳng thắn kì lạ về số lượng lớn dữ liệu đồng vị bao gồm cách giải thích người Neandertal chủ yếu sống dựa vào thực vật thủy sinh đến việc ăn thịt lẫn nhau, cả hai quan điểm này trái ngược với các bằng chứng khảo cổ học. Các phép đo đồng vị đặc trưng cho hợp chất mới này khẳng định lại các giải thích trước đây về chế độ ăn của người Neandertal bao gồm chủ yếu là động vật ăn cỏ lớn, mặc dù tất nhiên họ cũng tiêu thụ các loại thực phẩm khác như thực vật.
Chế độ dinh dưỡng đơn điệu
Ngoài việc xác nhận người Neandertal là động vật ăn thịt trên cạn, nghiên cứu này dường như chỉ ra rằng những Tông người này có chế độ ăn rất đơn điệu theo thời gian, ngay cả khi chúng đã bắt đầu thay đổi kĩ nghệ nguyên liệu, có thể dưới ảnh hưởng của người hiện đại. Em bé Neandertal của địa điểm Grotte du Renne được tìm thấy, thực sự có liên quan đến Châtelperronian, một kĩ nghệ đá tương tự như của người hiện đại. Do đó, người Neandertal muộn rất giống người hiện đại về các bức họa trong hang động và đeo vòng cổ, nhưng không giống như loài chị em của họ đó là dường như họ không thích đánh bắt cá.
Jean-Jacques Hublin, giám đốc Khoa Tiến hóa Người tại Viện Max Planck, nhận xét: “Nghiên cứu này xác nhận rằng khi người Homo sapiens đến châu Âu và gặp người Neandertal, họ đã cạnh tranh trực tiếp để khai thác các động vật có vú lớn “.Sahra Talamo- nhà nghiên cứu tại Viện Max Planck kết luận: “ Việc sử dụng hệ thống kết hợp các phân tích đồng vị đặc trưng cho hợp chất (CSIA) và định niên đại C sẽ giúp hiểu được liệu hai loài có thực sự có cùng một phương thức sinh kế trong những thời điểm quan trọng đó hay không.”
Nguồn: https://www.heritagedaily.com/2019/02/neandertals-main-food-source-was-definitely-meat/122703
Người dịch: Minh Trần
Các nhà nghiên cứu đã phát hiện một bình gốm cổ Nhật Bản giai đoạn Jomon muộn (4500-3300 BP) với khoảng 500 mọt ngô được đưa vào thiết kế của nó.

Mọt ngô là bọ cánh cứng thuộc phân họ Dryophthorinae, và là loài phá hoại thóc và ngũ cốc được lưu trữ. Trước năm 2003 *, các mảnh gốm và đồ gốm thời Jomon chứa các chất liệu in đã được thu thập bởi các nhà nghiên cứu từ nhiều địa điểm khảo cổ trên khắp Nhật Bản. Các điều tra về những hình in này cho thấy hàng trăm dấu vết hạt giống và côn trùng trên và trong đồ gốm. Trải qua nhiều năm, các nhà nghiên cứu phát hiện ra rằng mọt ngô chiếm hơn 90% tất cả các dấu in côn trùng được ghi nhận.
Năm 2010, Nhóm nghiên cứu của Giáo sư Obata, thuộc Đại học Kumamoto (KU) tại Nhật Bản đã tìm thấy những hình in mọt ngô trong đồ gốm 10.000 năm tuổi đã được phục chế ở đảo Tanegashima phía nam Nhật Bản. Họ chỉ ra mọt ngô, được nghĩ là đến từ Bán đảo Triều Tiên, đã làm hỏng thực phẩm lưu trữ như trứng cá và hạt dẻ, từ khá lâu trước khi việc trồng lúa bắt đầu trong khu vực này.
Vào năm 2012 *, nhóm nghiên cứu của đại học Kumamoto đã tìm thấy những hình in mọt ngô trong các mảnh gốm từ địa điểm Sannai-Maruyama ở quận Aomori phía bắc Nhật Bản. Hiện tượng mọt sống ở một khu vực có mùa đông lạnh là dấu hiệu cho sự phân phối thực phẩm bởi con người và môi trường trong nhà ấm áp tồn tại suốt mùa đông. Người ta cho rằng sự phá hoại của mọt ngô đối với thực phẩm được lưu trữ diễn ra mạnh mẽ trong thời kỳ Jomon.

(Trái). Con mọt ngô sống. (Phải). Hình ảnh hình in con một ngô trên bề mặt của mảnh gốm
Ảnh chụp bởi Prof. Hiroki Obata
Tiếp tục nghiên cứu về đồ gốm miền bắc Nhật Bản, nhóm nghiên cứu của giáo sư Obata, đã phát hiện ra những hình in mọt ngô đầu tiên ở Hokkaido và vào tháng 2 năm 2016 đã phát hiện ra một bình gốm chứa một số lượng lớn mọt ngô. Chụp CT X-quang để đếm các khoang côn trùng cho thấy rằng 417 mọt ngô trưởng thành được chứa trong các phần còn lại của bình gốm đó. Ngoài ra, nếu tất cả các mảnh còn thiếu được đếm, ước tính có tới 501con mọt được trộn vào đất sét và xuất hiện trong bình gốm khi nó còn nguyên khối.
Thật thú vị, khi so sánh kích thước cơ thể của 337 hình in mọt ngô được tìm thấy trên toàn quốc gia, nhóm nghiên cứu đã phát hiện ra rằng chiều dài cơ thể của mọt ngô ở miền đông Nhật Bản dài hơn khoảng 20% so với miền tây Nhật Bản. Người ta cho rằng sự khác biệt về chiều dài cơ thể này là do các giá trị dinh dưỡng khác nhau giữa các loại thực phẩm mà chúng nhiễm vào hạt dẻ ngọt của miền đông Nhật Bản so với trứng cá của miền tây Nhật Bản.
Hạt dẻ không có nguồn gốc từ Hokkaido và các nghiên cứu trước đây phỏng đoán rằng người đã mang chúng đến hòn đảo phía bắc Nhật Bản. Việc phát hiện mọt tại di chỉ khảo cổ Tatesaki ở Hokkaido là bằng chứng cho thấy người Jomon ở Tohoku (phía nam Hokkaido) mang theo các thực phẩm, bao gồm cả hạt dẻ bị nhiễm bởi mọt, qua eo biển Tsugaru bằng tàu
Giáo sư Obata nói “Ý nghĩa của một lượng lớn mọt ngô trưởng thành trong gốm không được đề cập chi tiết trong bài báo của tôi. Tuy nhiên, tôi tin rằng người Jomon đã trộn những con mọt vào đất sét gốm với hy vọng có một vụ mùa bội thu”.
Nguồn: https://www.heritagedaily.com/2018/12/ancient-japanese-pottery-includes-an-estimated-500-maize-weevils/122368
Người dịch: Minh Trần

(Trái). Bình gốm được khai quật ở di chi chỉ Tatesaki ở thị trấn Fukushima, Hokkaido với các hình in mọt ngô. (Phải). Các chấm vàng thể hiện các vị trí mọt ngô trên bình gốm.
Ảnh chụp bởi Prof. Hiroki Obata
Bình gốm này được phát hiện vào tháng 2 năm 2016 từ đống đổ nát ở Hokkaido, Nhật Bản. Sự phát hiện cực kỳ hiếm này cung cấp bằng chứng về việc trồng trọt và phân phối hạt dẻ, thực phẩm trong thời đại Jomon và tâm linh của người Nhật Bản cổ đại.Ảnh chụp bởi Prof. Hiroki Obata
Mọt ngô là bọ cánh cứng thuộc phân họ Dryophthorinae, và là loài phá hoại thóc và ngũ cốc được lưu trữ. Trước năm 2003 *, các mảnh gốm và đồ gốm thời Jomon chứa các chất liệu in đã được thu thập bởi các nhà nghiên cứu từ nhiều địa điểm khảo cổ trên khắp Nhật Bản. Các điều tra về những hình in này cho thấy hàng trăm dấu vết hạt giống và côn trùng trên và trong đồ gốm. Trải qua nhiều năm, các nhà nghiên cứu phát hiện ra rằng mọt ngô chiếm hơn 90% tất cả các dấu in côn trùng được ghi nhận.
Năm 2010, Nhóm nghiên cứu của Giáo sư Obata, thuộc Đại học Kumamoto (KU) tại Nhật Bản đã tìm thấy những hình in mọt ngô trong đồ gốm 10.000 năm tuổi đã được phục chế ở đảo Tanegashima phía nam Nhật Bản. Họ chỉ ra mọt ngô, được nghĩ là đến từ Bán đảo Triều Tiên, đã làm hỏng thực phẩm lưu trữ như trứng cá và hạt dẻ, từ khá lâu trước khi việc trồng lúa bắt đầu trong khu vực này.
Vào năm 2012 *, nhóm nghiên cứu của đại học Kumamoto đã tìm thấy những hình in mọt ngô trong các mảnh gốm từ địa điểm Sannai-Maruyama ở quận Aomori phía bắc Nhật Bản. Hiện tượng mọt sống ở một khu vực có mùa đông lạnh là dấu hiệu cho sự phân phối thực phẩm bởi con người và môi trường trong nhà ấm áp tồn tại suốt mùa đông. Người ta cho rằng sự phá hoại của mọt ngô đối với thực phẩm được lưu trữ diễn ra mạnh mẽ trong thời kỳ Jomon.

(Trái). Con mọt ngô sống. (Phải). Hình ảnh hình in con một ngô trên bề mặt của mảnh gốm
Ảnh chụp bởi Prof. Hiroki Obata
Tiếp tục nghiên cứu về đồ gốm miền bắc Nhật Bản, nhóm nghiên cứu của giáo sư Obata, đã phát hiện ra những hình in mọt ngô đầu tiên ở Hokkaido và vào tháng 2 năm 2016 đã phát hiện ra một bình gốm chứa một số lượng lớn mọt ngô. Chụp CT X-quang để đếm các khoang côn trùng cho thấy rằng 417 mọt ngô trưởng thành được chứa trong các phần còn lại của bình gốm đó. Ngoài ra, nếu tất cả các mảnh còn thiếu được đếm, ước tính có tới 501con mọt được trộn vào đất sét và xuất hiện trong bình gốm khi nó còn nguyên khối.
Thật thú vị, khi so sánh kích thước cơ thể của 337 hình in mọt ngô được tìm thấy trên toàn quốc gia, nhóm nghiên cứu đã phát hiện ra rằng chiều dài cơ thể của mọt ngô ở miền đông Nhật Bản dài hơn khoảng 20% so với miền tây Nhật Bản. Người ta cho rằng sự khác biệt về chiều dài cơ thể này là do các giá trị dinh dưỡng khác nhau giữa các loại thực phẩm mà chúng nhiễm vào hạt dẻ ngọt của miền đông Nhật Bản so với trứng cá của miền tây Nhật Bản.
Hạt dẻ không có nguồn gốc từ Hokkaido và các nghiên cứu trước đây phỏng đoán rằng người đã mang chúng đến hòn đảo phía bắc Nhật Bản. Việc phát hiện mọt tại di chỉ khảo cổ Tatesaki ở Hokkaido là bằng chứng cho thấy người Jomon ở Tohoku (phía nam Hokkaido) mang theo các thực phẩm, bao gồm cả hạt dẻ bị nhiễm bởi mọt, qua eo biển Tsugaru bằng tàu
Giáo sư Obata nói “Ý nghĩa của một lượng lớn mọt ngô trưởng thành trong gốm không được đề cập chi tiết trong bài báo của tôi. Tuy nhiên, tôi tin rằng người Jomon đã trộn những con mọt vào đất sét gốm với hy vọng có một vụ mùa bội thu”.
Nguồn: https://www.heritagedaily.com/2018/12/ancient-japanese-pottery-includes-an-estimated-500-maize-weevils/122368
Người dịch: Minh Trần
Khoảng 800 năm trước, một con tàu đã chìm ở biển Java ngoài khơi bờ biển của các đảo Java và Sumatra, Indonesia
Không có hồ sơ văn bản nào cho biết con tàu đã đi đâu hoặc xuất phát từ đâu, manh mối duy nhất là cấu trúc bị phân rã chủ yếu của tàu và hàng hóa của nó, được phát hiện dưới đáy biển vào những năm 1980. Kể từ khi phục dựng xác tàu đắm vào những năm 1990, các nhà nghiên cứu quốc tế đã cùng nhau hợp tác nghiên cứu tàu đắm biển Java coi đó là một phần của thế giới. Trong một nghiên cứu mới trên Tạp chí Khoa học Khảo cổ, các nhà khảo cổ học đã chứng minh một phương pháp mới cho biết đồ gốm của con tàu ban đầu đến từ đâu: bằng cách bắn gốm bằng súng X-quang.

Gốm trong bộ sưu tập tàu đắm biển Java của bảo tàng Field đang được phân tích bới máy huỳnh quang tia X. Ảnh được chụp bởi Kate Golembiewski.
Thật đáng ngạc nhiên khi chúng ta có thể xác định chính xác khu vực sản xuất vật liệu từ một vụ đắm tàu 800 năm tuổi, theo Wenpeng Xu, người đứng đầu nghiên cứu trên, sinh viên tốt nghiệp trường đại học Iilinois, Chicago, người đã tham gia chương trình tốt nghiệp chuyên ngành Nhân Chủng học với Bảo tàng Field.
“Nó giúp chúng tôi hiểu chi tiết về các mối quan hệ thương mại, việc biết cách con người tương tác trong quá khứ là rất quan trọng để chúng ta hiểu về hiện tại.”
Bảo tàng Field là nơi ước tính 7.500 mảnh hàng hóa được phục dựng từ tàu đắm, bao gồm 60 mảnh gốm được phân tích trong nghiên cứu này: bát và hộp làm bằng sứ được phủ trong một lớp men màu trắng xanh được gọi là qingbai. Dựa trên kiểu dáng của đồ gốm, các nhà khoa học biết rằng nó đến từ miền đông nam Trung Quốc, nhưng chỉ riêng kiểu dáng là chưa đủ để xác định chính xác nguồn gốc mảnh vì nhiều lò nung tạo ra những mảnh tương tự nhau. Bằng cách so sánh các thành phần hóa học của gốm từ tàu đắm và từ các lò nung khác nhau ở Trung Quốc, các nhà nghiên cứu đã có thể xác định chính xác hơn nơi gốm được sản xuất
Gốm ở các di chỉ khác nhau có thành phần hóa học khác nhau do sự thay đổi của các yếu tố có trong đất sét vùng đó hoặc trong các công thức mà thợ gốm sử dụng để trộn đất sét của họ. Nếu một mảnh gốm của tàu đắm khớp với đồ gốm tìm thấy tại một địa điểm khảo cổ, thì dự đoán khá an toàn rằng đồ gốm có nguồn gốc từ địa điểm đó. “Mỗi di chỉ lò nung sử dụng nguyên liệu và thành phần riêng cho đất sét, đó là cái tạo nên dấu vấn tay độc nhất cho mỗi mẫu”, Xu giải thích. “ Nếu dấu vân tay của mẫu khớp với dấu vân tay của lò nung, thì rất có thể đó là nơi sản xuất ra mẫu đó.” Đây là nơi mà súng X-quang can thiệp.
Lisa Niziolek, nghiên cứu viên Bảo tàng Field và là đồng tác giả của nghiên cứu trên cho biết, “Chúng tôi đã sử dụng một máy dò huỳnh quang tia X xách tay. Nó trông rất giống một khẩu súng bắn tia. Khoa học đằng sau phân tích thành phần rất phức tạp, nhưng Niziolek đã đánh bại nó: “Bạn đang bắn tia X vào một chất liệu mà bạn quan tâm. Nó kích thích các nguyên tử của chất liệu đó. Năng lượng bắn ra ngoài, điều này cho phép đo năng lượng đó. Các yếu tố khác nhau có các kí hiệu năng lượng bắn ra khác nhau.”
Biết được nguồn gốc chính xác của hàng hóa trên tàu cho thấy quy mô và sự phức tạp của các mạng lưới thương mại tại thời điểm đó. Các đồ gốm trong nghiên cứu này đã được sản xuất cách nơi con tàu chìm hơn 2.000 dặm – xấp xỉ khoảng cách giữa New York và Las Vegas.
“Một vấn đề quan trọng nổi bật đó là tàu đắm cho chúng ta biết rằng có những mạng lưới thương mại khổng lồ trong thế kỷ 12 và 13.” Chuyên gia nhân chủng bảo tàng Field và là đồng tác giả nghiên cứu, Gary Feinman nói. “Chúng tôi được dạy để liên kết các mạng lưới thương mại rộng lớn với người châu Âu như Magellan và Marco Polo, nhưng người châu Âu không là một phần lớn của mạng lưới đi từ châu Á đến châu Phi này. Toàn cầu hóa không chỉ là một hiện tượng gần đây. Nó không chỉ là tập trung ở châu Âu, không chỉ gắn liền với chủ nghĩa tư bản hiện đại. Thế giới cổ đã được kết nối với nhau nhiều hơn mọi người nghĩ.”
Niziolek cho biết “Mọi người thường coi các vụ đắm tàu là các hộp thời gian, nhưng tàu đắm biển Java còn ý nghĩa hơn thế”. “Một hộp thời gian đại diện cho một khoảnh khắc đóng băng đúng lúc, nhưng điều đó bỏ qua cách các kết quả trên tiết lộ những mạng lưới kinh tế xã hội thay đổi và rộng lớn này.”
Feinman đồng ý: “Gần như đối lập với một hộp thời gian đẹp, bị bao bọc, nó giống như một cửa sổ mở ra một chân trời rộng và cho chúng ta biết vật liệu đó đã lên con tàu này như thế nào trước khi chìm.”
Người dịch: Minh Trần
Nguồn (https://www.heritagedaily.com/2019/02/x-ray-gun-helps-researchers-pinpoint-the-origins-of-pottery-found-on-ancient-shipwreck/122667)
- Luận á n Tiến sĩ Khảo cổ học
n Tiến sĩ Khảo cổ học
- Tác giả: Nguyễn Hồng Ân
- Mã số: 62220317
- Hà Nội-2016
- Người hướng dẫn khoa học:
+ PGS.TS Phạm Đức Mạnh
+ PGS.TS Nguyễn Giang Hải
Ngoài phần mở đầu và kết luận, phụ lục bản ảnh, bản vẽ, bản đồ v.v... luận án gồm 3 chương:
Chương 1: Tổng quant ư liệu
Chương 2: Các di tích khảo cổ học Cự thạch ở Đồng Nai
Chương 3: Quần thể di tích khảo cổ học Cự thạch Đồng Nai trong khung cảnh Việt Nam và châu Á.
Xin trân trọng giới thiệu!!
 n Tiến sĩ Khảo cổ học
n Tiến sĩ Khảo cổ học- Tác giả: Nguyễn Hồng Ân
- Mã số: 62220317
- Hà Nội-2016
- Người hướng dẫn khoa học:
+ PGS.TS Phạm Đức Mạnh
+ PGS.TS Nguyễn Giang Hải
Ngoài phần mở đầu và kết luận, phụ lục bản ảnh, bản vẽ, bản đồ v.v... luận án gồm 3 chương:
Chương 1: Tổng quant ư liệu
Chương 2: Các di tích khảo cổ học Cự thạch ở Đồng Nai
Chương 3: Quần thể di tích khảo cổ học Cự thạch Đồng Nai trong khung cảnh Việt Nam và châu Á.
Xin trân trọng giới thiệu!!
Ngô Thị Nhung
- Luận án Tiến sĩ Khảo cổ học
Tiến sĩ Khảo cổ học
- Tác giả: Lê Hải Đăng
- Mã số: 62220317
- Hà Nội-2017
- Người hướng dẫn khoa học:
+ PGS.TS Trình Năng Chung
+ TS. Nguyễn Gia Đối
Khảo cổ học thời đại đá ở khu vực thượng du sông Đà là luận án tiến sĩ chuyên ngành khảo cổ học của TS. Lê Hải Đăng, hiện đang công tác tại Viện Khảo cổ học.
Ngoài phần mở đầu và kết luận, phụ lục bản ảnh, bản vẽ, bản đồ v.v... luận án gồm 4 chương:
Chương 1: Tổng quan tư liệu
Chương 2: Hệ thống di tích thời đại Đá thượng du sông Đà
Chương 3: Đặc trưng, tính chất, niên đại của các giai đoạn phát triển văn hóa
Chương 4: Thời đại Đá khu vực thượng du sông Đà: Đời sống vật chất, tinh thần, tổ chức xã hội và các mối quan hệ.
Xin trân trọng giới thiệu!!
 Tiến sĩ Khảo cổ học
Tiến sĩ Khảo cổ học- Tác giả: Lê Hải Đăng
- Mã số: 62220317
- Hà Nội-2017
- Người hướng dẫn khoa học:
+ PGS.TS Trình Năng Chung
+ TS. Nguyễn Gia Đối
Khảo cổ học thời đại đá ở khu vực thượng du sông Đà là luận án tiến sĩ chuyên ngành khảo cổ học của TS. Lê Hải Đăng, hiện đang công tác tại Viện Khảo cổ học.
Ngoài phần mở đầu và kết luận, phụ lục bản ảnh, bản vẽ, bản đồ v.v... luận án gồm 4 chương:
Chương 1: Tổng quan tư liệu
Chương 2: Hệ thống di tích thời đại Đá thượng du sông Đà
Chương 3: Đặc trưng, tính chất, niên đại của các giai đoạn phát triển văn hóa
Chương 4: Thời đại Đá khu vực thượng du sông Đà: Đời sống vật chất, tinh thần, tổ chức xã hội và các mối quan hệ.
Ngô Thị Nhung
Nhà x uất bản: Nhà xuất bản Khoa học xã hội
uất bản: Nhà xuất bản Khoa học xã hội
Năm xuất bản: 2017
Kích thước: 14.5 x 20.5 cm
Số trang: 262
Cuốn sách trình bày một cách có hệ thống về thiết chế chính trị - pháp lý Việt Nam thời Lê sơ giai đoạn 1428-1527, đặc biệt là dưới thời Lê Thánh Tông trị vì. Đối tượng nghiên cứu là các quan hệ xã hội cơ bản trong xã hội thời Lê sơ; hệ tư tưởng và hệ thống các quy định nền tảng của thiết chế chính trị - pháp lý thời Lê sơ; tổ chức và hoạt động của các bộ phận cấu thành thiết chế chính trị - pháp lý. Cuốn sách nhằm tìm hiểu những giá trị lịch sử và đương đại của thiết chế chính trị - pháp lý thời Lê sơ, trên cơ sở đó đề xuất những giải pháp nhằm tiếp thu hợp lý những giá trị đó trong quá trình xây dựng và hoàn thiện nhà nước pháp quyền XHCN ở nước ta hiện nay.
Nội dung chính của cuốn sách bao gồm 4 chương:
Chương 1: Tổng quan tình hình nghiên cứu và cơ sở lý thuyết.
Chương 2: Nhận diện thiết chế chính trị - pháp lý thời Lê sơ.
Chương 3: Cơ chế vận hành của thiết chế chính trị - pháp lý thời Lê sơ và tác động của nó đến xã hội Việt Nam đương thời.
Chương 4: Giá trị đương đại của thiết chế chính trị - pháp lý thời Lê sơ đối với quá trình xây dựng nhà nước pháp quyền Xã hội chủ nghĩa Việt Nam hiện nay.
Cuốn sách được Nhà xuất bản Khoa học xã hội ấn hành năm 2017.
Xin trân trọng giới thiệu!!
 uất bản: Nhà xuất bản Khoa học xã hội
uất bản: Nhà xuất bản Khoa học xã hộiNăm xuất bản: 2017
Kích thước: 14.5 x 20.5 cm
Số trang: 262
Cuốn sách trình bày một cách có hệ thống về thiết chế chính trị - pháp lý Việt Nam thời Lê sơ giai đoạn 1428-1527, đặc biệt là dưới thời Lê Thánh Tông trị vì. Đối tượng nghiên cứu là các quan hệ xã hội cơ bản trong xã hội thời Lê sơ; hệ tư tưởng và hệ thống các quy định nền tảng của thiết chế chính trị - pháp lý thời Lê sơ; tổ chức và hoạt động của các bộ phận cấu thành thiết chế chính trị - pháp lý. Cuốn sách nhằm tìm hiểu những giá trị lịch sử và đương đại của thiết chế chính trị - pháp lý thời Lê sơ, trên cơ sở đó đề xuất những giải pháp nhằm tiếp thu hợp lý những giá trị đó trong quá trình xây dựng và hoàn thiện nhà nước pháp quyền XHCN ở nước ta hiện nay.
Nội dung chính của cuốn sách bao gồm 4 chương:
Chương 1: Tổng quan tình hình nghiên cứu và cơ sở lý thuyết.
Chương 2: Nhận diện thiết chế chính trị - pháp lý thời Lê sơ.
Chương 3: Cơ chế vận hành của thiết chế chính trị - pháp lý thời Lê sơ và tác động của nó đến xã hội Việt Nam đương thời.
Chương 4: Giá trị đương đại của thiết chế chính trị - pháp lý thời Lê sơ đối với quá trình xây dựng nhà nước pháp quyền Xã hội chủ nghĩa Việt Nam hiện nay.
Cuốn sách được Nhà xuất bản Khoa học xã hội ấn hành năm 2017.
Xin trân trọng giới thiệu!!
Ngô Thị Nhung
 Nhà xuất bản: Nhà xuất bản Chính trị Quốc gia sự thật
Nhà xuất bản: Nhà xuất bản Chính trị Quốc gia sự thậtNăm xuất bản: 2017
Kích thước: 15,5 x 24 cm
Số trang: 556
Nhằm góp phần phổ biến kiến thức lịch sử dân tộc cho đông đảo bạn đọc, Nhà xuất bản Chính trị Quốc gia Sự thật phối hợp với Viện Sử học xuất bản bộ sách
Lịch sử Việt Nam phổ thông của tập thể các nhà khoa học, các tác giả đã trình bày toàn bộ tiến trình lịch sử dân tộc từ khởi thủy đến năm 2000 thông qua các chuyên đề ngắn gọn, súc tích nhưng đầy đủ thông tin cần thiết, dễ đọc, dễ hiểu, dễ nhớ. Bộ sách gồm 9 tập:
Tập 1: Từ tiền sử đến khởi nghĩa Hai Bà Trưng
Tập 2: Từ khởi nghĩa Hai Bà Trưng đến thế kỷ X
Tập 3: Từ thế kỷ X đến năm 1593
Tập 4: Từ năm 1593 đến năm 1858
Tập 5: Từ năm 1858 đến năm 1930
Tập 6: Từ năm 1930 đến năm 1945
Tập 7: Từ năm 1945 đến năm 1954
Tập 8: Từ năm 1954 đến năm 1975
Tập 9: Từ năm 1975 đến năm 2000
Lịch sử Việt Nam phổ thông, Tập 7: Từ năm 1945 đến năm 1954 trình bày những vấn đề, những sự kiện cơ bản nhất trong lịch sử Việt Nam từ sau Cách mạng Tháng Tám năm 1945 đến chiến thắng Điện Biên Phủ năm 1954. Toàn bộ tiến trình lịch sử Việt Nam từ năm 1945 đến năm 1954 đã được phản ánh phong phú, sinh động và chân thực trong tập sách mới. Tập sách gồm 4 chương, thuận tiện cho việc theo dõi và tra cứu các sự kiện, nhân vật, vừa bảo đảm tính lôgíc, vừa tuân thủ nghiêm cẩn tính khách quan và sự chân thực của lịch sử.
Xin trân trọng giới thiệu!!
Tập 1: Từ tiền sử đến khởi nghĩa Hai Bà Trưng
Tập 2: Từ khởi nghĩa Hai Bà Trưng đến thế kỷ X
Tập 3: Từ thế kỷ X đến năm 1593
Tập 4: Từ năm 1593 đến năm 1858
Tập 5: Từ năm 1858 đến năm 1930
Tập 6: Từ năm 1930 đến năm 1945
Tập 7: Từ năm 1945 đến năm 1954
Tập 8: Từ năm 1954 đến năm 1975
Tập 9: Từ năm 1975 đến năm 2000
Lịch sử Việt Nam phổ thông, Tập 7: Từ năm 1945 đến năm 1954 trình bày những vấn đề, những sự kiện cơ bản nhất trong lịch sử Việt Nam từ sau Cách mạng Tháng Tám năm 1945 đến chiến thắng Điện Biên Phủ năm 1954. Toàn bộ tiến trình lịch sử Việt Nam từ năm 1945 đến năm 1954 đã được phản ánh phong phú, sinh động và chân thực trong tập sách mới. Tập sách gồm 4 chương, thuận tiện cho việc theo dõi và tra cứu các sự kiện, nhân vật, vừa bảo đảm tính lôgíc, vừa tuân thủ nghiêm cẩn tính khách quan và sự chân thực của lịch sử.
Xin trân trọng giới thiệu!!
Ngô Thị Nhung
Trang
Copyright © 2016 by khaocohoc.gov.vn.
Thiết kế bởi VINNO
Tổng số lượt truy cập: 10683638
Số người đang online: 20
